AMRs vs. AGVs: The Differences Explained
Conger
MAY 11, 2022
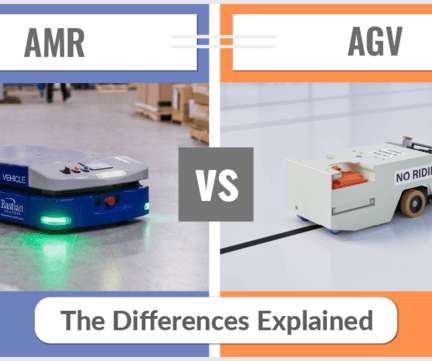
AGVs are automated material handling equipment that follows predefined paths with limited ability to make real-time corrections to its course. AMRs are automated material handling equipment that use digital maps or sensors to navigate its environment, while being able to make real-time course correction. Unit-Load AGVs.










Let's personalize your content