Edge Computing in Logistics: Enabling Real-Time Data Processing Closer to Operations
Logistics Viewpoints
APRIL 28, 2025
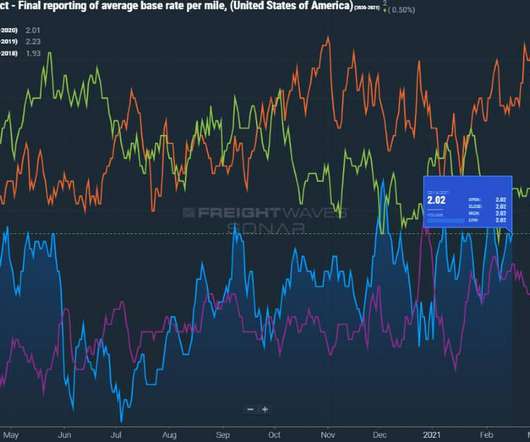
As logistics networks become increasingly complex, the volume of real-time data generated by devices, equipment, vehicles, and facilities is growing rapidly. Edge computing processing data locally, near the source has emerged as a method to address these challenges by reducing latency and improving resiliency.












































Let's personalize your content