Interoperability in the Supply Chain: Leveraging the OSI Model for Seamless Logistics
Logistics Viewpoints
NOVEMBER 27, 2024
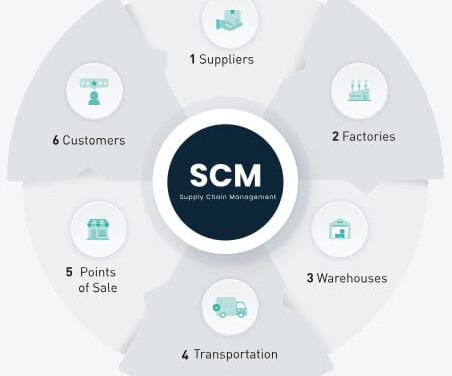
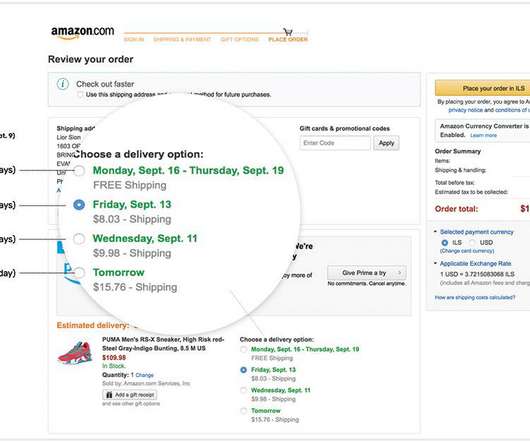
By applying the ISO OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) seven layer model, traditionally used in networking, to logistics, businesses can achieve a structured framework that enhances communication, reduces friction, and improves collaboration throughout the supply chain. Presentation Layer: Translates between data formats.











































Let's personalize your content